What is uterine fibroids, why is it dangerous, its symptoms and methods of treatment. Uterine fibroids - what is it, causes, first signs, symptoms, treatment and complications Uterine fibroids symptoms and signs treatment
Many diseases of the organs of the female reproductive system are directly related to the hormonal processes occurring in the body. Pathologies arise due to an imbalance of female sex hormones, as well as the factors that cause it. Such violations can become, in particular, the cause of fibroids and other benign and even malignant neoplasms in the uterus. Signs of the disease may not appear immediately. The more it is started, the more difficult the treatment and the greater the likelihood of complications.
Content:
Myoma of the uterus and its types
Myoma is a tumor of a benign nature, formed from the muscle and connective tissue of the uterus. Most often it appears in women after 30-40 years. In most cases, there are no obvious signs of uterine fibroids. Therefore, preventive examinations by a gynecologist play an important role. Ultrasound helps to notice the tumor.
This tumor is hormone-dependent, that is, under the influence of female sex hormones, its growth begins. Therefore, it begins to increase during pregnancy, when the ratio of hormones in the blood changes dramatically, as well as in obesity. Adipose tissue is capable of producing estrogen, as are the ovaries. Exceeding the level of these hormones leads to improper development of cells, the emergence of pathological neoplasms.
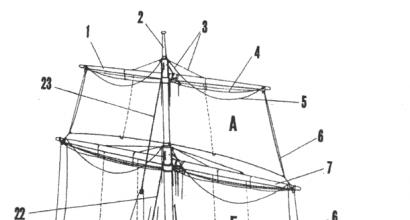
Fibroids are nodules in the myometrium (muscle fibers). The formation of a tumor occurs from one atypical cell, which then begins to divide, causing the growth of the neoplasm. There are various options for the growth of a tumor in the uterus. Depending on the direction of development, the following types of fibroids are distinguished:
- Interstitial. Formed in the thickness of the myometrium.
- Submucosal (or submucosal). It grows from the muscle towards the lining of the uterus.
- Subserous. Grows in the direction of the abdominal cavity.
- Intraligamentary - formed between the ligaments of the uterus.
The occurrence of uterine fibroids usually occurs in her body, but in rare cases it is also possible in the cervix. Fibroids that develop in muscle tissue are considered typical, and those that form in the neck or on the ligaments are considered an atypical form of the disease.
Neoplasms that extend onto the inner or outer surface of the uterus (submucosal and subserous fibroids) are a thickening on a stalk penetrated by blood vessels. There are single nodes that, when growing, can fill the entire uterus, even go into the peritoneal region. Most often, fibroids appear in the form of several nodes of different sizes. At the same time, the shape of the uterus changes, its weight increases.
Video: Why fibroids occur. Symptoms and treatment
Factors contributing to the formation of a tumor
Myoma appears as a result of a single cell mutation. Its further division and development of the tumor is affected by changes in the hormonal background in the body, a violation of the ratio of estrogens and progesterone. During menopause, when the production of female sex hormones decreases, the tumor may disappear on its own.
In addition, the cause of the formation of nodes in the uterus are:
- Metabolic disorders, diseases of the liver, pancreas, diabetes mellitus.
- Presence of hypertension, especially in those younger than 35 years of age.
- Inflammatory processes in the cervix and uterine cavity.
- Obesity, which contributes to malnutrition, lack of physical activity. The risk of such a tumor is less in women whose diet is dominated by vegetables, fruits, greens, or low-calorie animal products.
- The time of the appearance of the first menstruation, the onset of sexual activity. Early menopause also provokes the formation of this tumor.
- The presence of pregnancies (term and interrupted). The likelihood of fibroid formation is lower in women who have given birth at least once, who have breastfed for more than six months.
- The cause of uterine fibroids may be damage to the endometrium during an abortion, the installation of an intrauterine device. Injury to the mucosa also occurs during curettage for the purpose of diagnosing and treating gynecological diseases (endometriosis, cyst formation, polyps).
- Constant nervous overload and depression can contribute to the occurrence of hormonal disorders. City women live in a more intense rhythm, so they have fibroids more often than rural women. The environmental situation in the city is also more difficult. The probability of occurrence of cellular mutations is increased here.
- The most important role is played by heredity.
Warning: Myoma most often occurs against the background of other serious diseases. It can grow rapidly, which greatly complicates the treatment. To avoid serious consequences, it must be diagnosed as early as possible, without postponing a visit to the doctor and without wasting time on self-healing.

Symptoms and signs
Obvious symptoms of the disease may appear if the neoplasm is already large enough. At an early stage, when it would seem that there are no reasons for the formation of uterine fibroids, a woman may not be aware of her presence. There may be a slight feeling of heaviness in the lower part of the abdomen, discomfort during intercourse.
As the size of the tumor increases and new nodes form, the discomfort increases more and more. One of the first symptoms of trouble is a change in the nature of menstruation. Their duration increases to 8-10 days. There are significant fluctuations in the duration of pauses between periods. Menstrual flow becomes profuse, contains blood clots. There may be spotting between periods.
The growing tumor puts pressure on the bladder, so there are frequent urges to urinate, it becomes more difficult. Pressure on the intestines leads to constipation, bloating. Compression of the nerve endings in the pelvic organs causes pain that radiates to the back and legs.
There is a growing feeling of heaviness, the presence of something foreign in the stomach. Sexual contact becomes painful (in the case of the location of the nodes from the side of the vagina). The belly grows, as during pregnancy. The sprain increases the pulling pain in the abdomen.
As a result of abundant blood loss, anemia occurs (lack of hemoglobin in the blood, leading to oxygen starvation of cells). A woman has signs such as pallor, weakness, dizziness, heart rhythm disturbance, headaches.

Myoma, unlike a cancerous tumor, grows slowly, so the chances of detecting it by the first signs are much greater.
Complications
A growing tumor compresses the blood vessels, which leads to disruption of its blood supply. The result is the death of tumor tissue (necrosis) or the formation of areas of suppuration. At the same time, the content of leukocytes in the blood increases in a woman. The body temperature rises.
A serious complication is twisting of the stem of the superficial node. In this case, there is also a violation of blood flow and the formation of tissue necrosis. This pathology is manifested by sharp spasmodic pain.
The degeneration of fibroids into a malignant tumor (sarcoma) is rare. Malignant degeneration may be indicated by the rapid growth of the tumor, especially during menopause, when it generally appears extremely rarely. Therefore, if even a small fibroid is detected, it is necessary to regularly do an ultrasound scan to monitor its condition.
As a result of menstrual heavy and prolonged bleeding, anemia occurs - a condition dangerous to health, leading to disruption of the work of all organs and systems of the body.
Such a tumor can cause infertility or miscarriage, since the growth of nodes and changes in the shape of the uterus interfere with the normal progress of the fertilized egg and its attachment to the endometrium.

uterine fibroids during pregnancy
Pregnancy can trigger the formation of such tumors. If they appeared earlier in a woman, then their growth during this period usually stops (the diameter reaches a maximum of 5 cm). A woman is worried about nausea, occasionally - a slight increase in temperature.
However, there is a risk of the following complications:
- childbirth before 37 weeks if the fibroid is located near the placenta, especially when there are several nodes;
- spontaneous abortion at an early stage;
- partial detachment of the placenta, accompanied by bleeding;
- incorrect presentation of the fetus due to deformation of the uterus;
- decreased ability of the uterus to contract normally during childbirth.
Therefore, usually in the presence of uterine fibroids, a woman is given a caesarean section. It is also possible to remove nodes. After such an operation, infertility does not threaten. She may subsequently become pregnant and give birth to a healthy child. During pregnancy, fibroids do not affect the development of the fetus, and cannot cause its intrauterine death.
Video: Symptoms of fibroids, complications after treatment
Treatment
The main goal of treatment is to eliminate the cause of the disease and the harmful effects of the tumor on the surrounding tissues of the uterus, reduce its size, stop growth. Both medical and surgical methods are used.
Drugs are prescribed in accordance with the cause and manifestations of the disease. It is possible to use antibiotics (to eliminate inflammatory processes), hormonal drugs (in order to restore the balance of hormones, normalize the menstrual cycle). A woman is prescribed treatment with iron preparations against anemia, as well as complex vitamins (especially A, E, C), which also contain zinc, iodine, and copper. They help accelerate the regeneration of endometrial cells destroyed by the tumor, increase the body's defenses. If necessary, painkillers and sedatives are used.
Note: Hormonal preparations are selected individually after a blood test for hormones. Violation of the treatment regimen or dosage may lead to the opposite effect. Uncontrolled treatment of fibroids with herbs or herbal remedies is unacceptable.
Surgical treatment is used in cases where the node is large, the myoma is accompanied by bleeding, anemia. The operation is performed if the tumor grows rapidly, interferes with urination or bowel function, and also blocks the cervix.
The consequence of the operation may be infertility due to the formation of scars and adhesions in the uterus. Therefore, in childbearing age, medications are more often used. In older women, fibroids are removed if they grow rapidly.
Methods such as myomectomy (removal of tumor nodes, preservation of the uterus) and the method of embolization of the uterine arteries (cessation of the blood supply to the tumor by blocking the vessels, after which the fibroid dries out) are used.
Video: Principles of treatment of fibroids. Indications for surgery
Uterine fibroids what to do - once again a sobbing woman in line to the doctor asks her interlocutors in desperation.
Of course, fibroids are the subject of a very serious disease of the female body, but not fatal. It develops during the period when a woman can give birth, depends on the hormonal background.
Uterine fibroids what to do for a woman:
This is a benign tumor without a threat to the life of a woman, shaped like a pear. It develops in the muscular layer of the diseased uterus.
It is natural to observe its development and be treated if necessary. Fibroids grow slowly, when menopause ends, they disappear. It is a chronic disease of the muscular wall of the uterus.
We have to get acquainted with fibroids, find out how it arose, its causes, symptoms of the disease, how to treat it correctly, in what time frame.
What to do with uterine fibroids, symptoms:
Everyone who has it discovered will want to know how she will feel, what to pay attention to?
A very large percentage in our time suffer from it - up to 85%. Most of its small size does not feel anything at all. Usually, outward-growing nodes, even large ones, develop without any symptoms.
The most dangerous internal nodes (in the wall of the uterus or its cavity).
As she grows:
- She can put pressure on the organs located in the neighborhood - it will seem to a woman that she is pregnant.
- Growing fibroids can compress blood vessels, then there is pain in the lower abdomen, a rise in body temperature.
- The contractile function of the uterus is disturbed - heavy periods begin. This is perhaps the very first symptom in women. Often prolonged, irregular, with vaginal leucorrhea. Symptoms of anemia with blood loss during menstruation are very pronounced (dizziness, weakness).
- When squeezing the fallopian tubes, there is a high risk of remaining infertile.
- During pregnancy, the threat of miscarriage, miscarriage due to compression by the tumor may increase.
- You can feel a knot in the lower abdomen that looks like a foreign body. The abdomen increases in size.
- Unpleasant symptoms during sex, urination.
- Constipation occurs due to compression of the rectum.
Usually, fibroids are discovered absolutely by chance at a gynecologist or ultrasound.
What to do with uterine fibroids, causes of appearance:
- Doctors believe that a very high risk of developing fibroids in nulliparous women, pregnancy reduces the risk of fibroids.
- , obesity change the hormonal background of a woman for the worse. Patients with diabetes are also at risk.
- Early onset of the menstrual cycle, estrogen affects the formation of fibroids, as does progesterone (a hormone).
- Late first pregnancy, reduced breastfeeding time.
- Taking hormone replacement therapy c.
- Even phytoestrogens in food can negatively affect the growth of uterine fibroids or preparations containing them "qi-clim".
- Any irradiation.
- Patients with hypertension due to damage to the smooth muscles of the uterus.
- Uterine trauma: abortion or surgery.
- Infectious diseases (, ureplasma).
- Heredity of the disease: 30 - 40 percent of cases.
For violations of a healthy lifestyle:
- Lots of caffeine.
- Little sleep.
- Alcohol, nicotine change the level of endogenous hormones for the worse. Everyone who quit this habit got rid of the risk of developing fibroids up to 50%.
- Prolonged stress.
- Fatty, fried, smoked, salty food with preservatives.
- Lack of fruits, vegetables, greens, vitamins and minerals (vitamins A, D) in food. Lack of citrus. Food with lycopene (a powerful antioxidant) reduces the size of fibroids, their size.
- Refined food with a high glycemic index.
- Lots of red meat on the menu (beef, lamb). Few fish.
- Physical activity reduces the risk of fibroids in acceptable numbers. Health, weight, blood counts are preserved.
- A diet rich in vegetables and fruits with fiber reduces the risk of developing fibroids.
The main soil for the formation of a tumor is prepared by estrogen (the female hormone), and progesterone (the second female hormone) completes the work.
What to do with uterine fibroids, its classification:
In medicine, its development is divided into:
By the number of nodes in the uterus:


- Single.
- Multiple nodes.
They classify her by weeks of pregnancy, a woman feels this way. You probably saw in your medical record 4 or 5 weeks of pregnancy or more. So gynecologists determine its size. There are nodes reaching 38 weeks of pregnancy in size.
Origin:
- Leiomyoma.
- Lipomyoma.
- Rhabdomyoma.
- Fibromyoma.
I'm sure you've heard of many of them already. The name depends on which layer of the uterus the developing tumor is located.


- Submucosal (submucosal), will develop into the uterine cavity.
- Intramural or (interstitial), located in the muscle layer of the diseased uterus.
- Subserous: nodes on the outside closer to the peritoneum. Such knots can be on a leg.
Diagnosis of uterine fibroids:
It is diagnosed by ultrasound (ultrasound):
- The dimensions are clearly visible.
- Where is it.
- Number of nodes.
- It is important to determine the blood flow of the myomatous node.
CT (computed tomography), rarely applicable, provides no more information than ultrasound.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is used to a limited extent for large nodes.


- I think that a woman with fibroids needs to know the prohibited actions or their restrictive option.
- All thermal procedures: heating, bath, sauna, heating pads, baths. Warming up the body will lead to tumor growth.
What needs to be done:
- To reduce the risk of fibroids, you need to have sex, and with a discharge at the end. Sex should be regular.
- With increased nervous excitability, drink tinctures of valerian, mint, motherwort. Hormone levels are regulated.
- Lose your extra pounds, treat sores on time, follow a healthy lifestyle.
- Women's sores should be under constant control and treatment.
- Once every 12 months, find time and go to see a gynecologist, undergo an ultrasound for any suspicion of trouble in your beloved.
Uterine fibroids what to do how to treat:
In medicine, there are two main methods of treatment:
Operation (surgery):


- It consists in removing the uterus completely.
- A gentle method is the removal of the node (if there are a small number of them and the woman has not yet given birth).
- Embolization of the uterine arteries - in fact, the blood supply to the nodes is blocked. Nodes shrink, decrease, disappear. Often the nodes become inflamed, up to their necrosis. Sometimes node growth is reversible.
- The method of ultrasonic fuzooblation (a method of evaporating a node with ultrasound) is a fairly new direction in the treatment of fibroids. But the method is rarely used due to the high probability of damage to neighboring organs.
Medication treatment:
- Hormonal contraceptives to prevent the formation of nodes. To slow down their growth, only up to 1.5 centimeters in size. They help keep small knots under control. If the sizes are larger, the treatment is different.
- Mirena hormonal coil, actively fights active menstruation with myoma. With nodes growing into the uterine cavity, the spiral is contraindicated.
- Treatment with special drugs, when a woman capable of giving birth is sent for a while to an artificial menopause. Her menstruation stops, the nodes stop growing. Deliberately I will not name the drugs, the treatment is very serious.
- You just need to understand that when you stop taking such drugs, the nodes begin to grow again. Treatment lasts no more than six months, no more. The absence of menstruation is fraught with the health of the patient. Such treatment is carried out in time with natural menopause according to indications. Young women are not prescribed this treatment.
Official medicine is categorical - no treatment will help with uterine myoma anymore. However, I will offer you some of the most effective traditional medicine recipes according to reviews.
No treatment with indoles and epigalates will save from the growth of fibroids.
Uterine fibroids what to do, operation:
- With small sizes of nodes, it is not treated in any way - they are simply observed.
- With the growth of fibroids and its location in the neck, an operation is performed.
- There is no need to be afraid, with sizes up to 10 weeks, the operation is performed by the laparoscopic method (three punctures on the abdomen, sizes up to 1 cm).
- The next day they get out of bed.
- Up to three days, drainage tubes are in the stomach, then they are removed from them. You can move with them, it doesn't interfere at all.
- Up to five days they are not allowed to eat, they are fed through droppers. Hunger is not felt.
- They inject antibiotics, take aspirin to thin the blood (blood loss during operations is inevitable).
- Discharged on the tenth day.
- For women in menopause, all female organs are removed, except for the cervix (hystorectomy).
- There is nothing wrong with that, you were and will remain a woman.
- You will experience even more pleasure in bed and nothing will change for your man.
- The cervix was saved for physiology.
- For dry vaginal mucosa with menopause, buy a water-based intimate lubricant at the pharmacy. The pain will disappear. The man applies lubricant on the penis or condom.
- Do not panic and be treated, if the size and location of the nodes allow, observe them before menopause. They disappear at menopause.
- If surgery is indicated, do it.
- There is nothing irreparable.
Uterine fibroids symptoms and treatment with folk remedies:
Surgical intervention is necessary only for large sizes of fibroids, while for small sizes it is simply observed or treated with medication. Only a doctor should do this.
This is a hormone-dependent disease, self-medication is contraindicated. Folk methods will be appropriate for very small tumor sizes and give excellent final results.
The simplest and most effective herbs and fees in the treatment of fibroids:
Hazel (hazelnut):
- It will take one glass of dry hazel leaves.
- Pour them into a thermos, adding one liter of boiling water.
- It is better to do the infusion at night.
- Strain in the morning.
- Drink in sips of a third of a glass up to four times / day.
- You can douching in the morning and evening.
Treat up to six months. The problem will go away.
In three weeks you will feel it.
Gradually, discomfort, pain will go away, the quality of life will improve.
Pine nuts:
- They are used for fibroids, mastopathy.
- You can just eat them in small portions peeled (up to 30 grams in the morning).
- With a large amount of use, weight increases.
- Fibroids are shrinking.
Sunflower oil treatment:
- Take a tablespoon of sunflower oil in your mouth in the morning.
- Do not swallow.
- Move it around in your mouth like you're rinsing your teeth.
- The procedure should be carried out for at least 25 minutes.
- Soon the oil will be very thin.
- You only need to spit it out when it turns white.
- This color will be from cleansing the body through the salivary glands from toxins and toxins.
- Rinse your mouth.
- Cleansing should be done once in the morning.
- You can take breaks and repeat.
- Exacerbations of sores during treatment take place.
Green tea:
- Invigorates, helps to get rid of excess testosterone (male hormone). Affects the causes of small breasts in women.
- Helps to fight hairiness of female legs.
- Possesses such activity - catechin of green tea.
Borova uterus (grass):


They are treated with a upland uterus for a long time. Infusions are used for oral administration, douching. There may be exacerbations of the disease, then improvement.
Recipe:
- Traditional preparation of decoction.
- One tablespoon of dry herb in a glass of boiling water.
- Keep in a water bath for about five minutes.
- We insist three hours.
- Douche in a warm form for up to 10 days (excluding the time of menstruation).
- Treat monthly.
Ingestion of decoction:
- We drink the decoction prepared in the same way one hour before meals.
- We begin to be treated from the fourth day of menstruation or immediately after menstruation.
- Dose: One tablespoon five times/day.
Alcohol tincture:
- Vodka 500 grams.
- Grass boron uterus 50 grams.
- Mix, insist better in the dark, no more than 21 days.
- Drink 40 drops before meals, three times is enough, starting from the fourth day of menstruation.
- Course 21 days.
- Break for seven days.
- Repeat again.
Be careful when treating boron uterus with gastritis, it is better to drink it after meals.
Red brush:


- Prepared in a water bath.
- One glass of boiling water is poured into a saucepan.
- Add the root of the red brush in a dose of a tablespoon.
- Hold 15 minutes.
- One hour after infusion, filter.
- Add boiling water to the volume of a full glass.
- A little honey is added.
- Drink a little a day before meals in equal portions three times.
- Course 45 days.
For the treatment of fibroids, propolis, burdock, and herbal preparations are used.
To summarize what has been written: what to do with uterine fibroids. If it exists, watch it.
With its active growth - delete and live. That's not fatal. Do not worry too much, you will not return anything. After the operation, you will live peacefully and happily.
Trust me, I'm telling you the truth.
Look more often at my site, I'm waiting for you.
Watch the video, treatment of fibroids with folk remedies:
Myoma is a benign tumor that grows from the connective tissue on the walls or in the uterine cavity. More often, women experience this trouble after 30-35 years. But recently, the disease often occurs in women of a younger age.
What is it - uterine fibroids, from what and why does it appear, how and with what can the disease be treated in the early stages (small sizes) and later?
general description
The disease occurs as a result of rapid and uncontrolled division of uterine cells. This process occurs due to increased secretion of estrogens (female sex hormones).
A blood test does not reveal a hormonal imbalance. Often, the disease can be the result of mechanical damage to muscle tissue (abortions, intrauterine devices, inflammation).
Fibroids are nodular neoplasms of various sizes appearing on the inner or outer surface of the reproductive organ. Multiple nodes are more common.
The size of such formations is considered in "weeks", as well as the size of the uterus at different stages of pregnancy. This allows you to accurately determine the growth of education. Usually the tumor is located inside the muscle layer.
Previously, there was an opinion that a benign formation (myoma) over time necessarily degenerates into a malignant one (cancer).
However, recent research disproves this theory. It has been scientifically proven that these diseases are formed from different tissues. Cancer may appear as a complication of fibroids, but this is quite rare.
Even a rapid increase in the size of a neoplasm is not always a sign of oncology. But to determine whether it is a benign tumor or not, it is possible only after a thorough examination.
Causes
The appearance of uterine fibroids can be triggered by many reasons. The main factor will be a high level of the hormone estrogen, low - progesterone.
To identify this, one blood test will not be enough. It is necessary to determine the hormonal status in general.
In addition to hormonal disorders common causes are:
- heredity;
- adenomyosis;
- diabetes;
- gynecological diseases;
- multiple abortions (including);
- hypertension;
- endocrine diseases;
- stress;
- obesity;
- bad ecology;
- use of intrauterine contraceptives;
- hypodynamia;
- chronic lesions of internal organs;
- lack of orgasm;
- irregular sex.
Women who have given birth have been shown to be less likely to develop knots. Often this neoplasm can appear during pregnancy. Especially if the first pregnancy is late.
important a woman's nutrition plays a role in the development of the disease.
The predominance of meat, fats, carbohydrates, sweets, fast food in the diet, lack of fiber increase the level of female hormones and contribute to obesity.
The use of fermented milk products, vegetables, cereals, fruits significantly reduces the possibility of developing a tumor.
Classification of species: what is it like
Depending on the size and location of nodes There are 3 types of uterine fibroids:
- or intramuscular - located in the middle of the muscle layer, characterized by large sizes;
- submucosal - grows inside the cavity, which leads to its deformation;
- subserous - located on the outside, grows into the abdominal cavity.
There is a separate type of disease - myoma "on the leg". It grows on a narrow or wide base, connecting it with the walls of the organ.
It can be submucosal or subserous, that is, located outside or inside the uterine cavity. Very rarely, a neoplasm can be located in the neck. Depending on the growth rate, there are simple and profiling.
According to the composition of the tumor is divided into fibroma(from connective tissue) and leiomyoma(from muscle).
Symptoms and signs: how to recognize in time
Small uterine fibroids at an early stage not accompanied by noticeable symptoms. You can find it at the next gynecological examination.

As uterine fibroids grow early signs may appear:
- prolonged, heavy and irregular menstruation;
- constipation;
- infertility;
- bleeding;
- anemia;
- frequent urination;
- heaviness and constant pain in the lower abdomen;
- spotting during intercourse;
- lower back pain;
- an increase in the abdomen is not associated with a significant increase in weight;
- frequent miscarriages.
What is dangerous uterine fibroids on the leg? When the “legs” are twisted, inflammation and rupture of the tumor occurs. This causes severe bleeding, acute pain in the lower abdomen, fever. This condition can be fatal.
The submucosal form of uterine fibroids during growth leads to persistent, incessant bleeding, in which there is a high risk of complication of the situation with iron deficiency anemia, everything is accompanied by sharp cramping pains.
Knots during pregnancy often lead to miscarriages or placental insufficiency.
Tumor growth during this period also causes fetal hypoxia, which can lead to premature or prolonged labor.
What to do, who to contact
It is impossible to self-identify the disease. When the above symptoms appear, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a gynecologist.
These signs may be accompanied by more dangerous diseases, such as cancer of the uterus or ovaries, endometriosis. To find out the cause of the ailment, it is necessary to undergo a complete medical examination.
In order not to start the disease, one must pass scheduled examination by a gynecologist at least twice a year.
Diagnostic measures

More often, the disease can be detected during a gynecological examination by an increase in the size of the uterus, thickening or deformation of its walls.
To determine the location and size of the tumor ultrasound of the genital organs.
What tests should be done for uterine fibroids? To exclude oncological diseases, a test for tumor markers, biochemical and hormonal blood tests are carried out.
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe hysteroscopy, X-ray, endoscopy, culdoscopy.
To get a complete picture of the disease, computed tomography, cervicoscopy and coagulation analysis are also used.
Methods and treatment regimens
Is it possible and how exactly to cure uterine fibroids? Therapy is carried out both surgically and conservatively.
At the initial stage of the disease, when the size of the tumor does not exceed 1-2 cm, drug treatment is used.
In the event of severe bleeding with pain and rapidly growing uterine fibroids, surgery is recommended.
If there are no symptoms of the disease, the size of the nodes is small, growth does not occur, then the treatment may consist in the constant observation of a specialist, diet, regular ultrasound examination.

With pain and medium-sized tumors hormonal drugs are prescribed. However, there are no drugs that completely eliminate the tumor.
All remedies can only temporarily alleviate the symptoms, reduce the size of the tumor nodes.
These drugs include:
- Antiprogestogens reduce tumor size and relieve symptoms. Used in preparation for surgery.
- Antigonadotropins: Nemestrane, Danazol. The size of the nodes does not reduce, but only eliminates the symptoms. These drugs are used extremely rarely, because they have many side effects: hair growth on the body and face, voice changes, acne.
GnRH agonists: Leuprorelin (Eligard, Prostap), Buserelin, Goserelin, Triptorelin (Diferelin). Apply such funds once a month to reduce the size of the tumor before surgery. The course of treatment is six months.
These drugs reduce the amount of estrogen in the body, but long-term use leads to osteoporosis. After the end of treatment, the nodes again begin to grow actively.
Oral contraceptives: Novinet, Rigevidon, Marvelon. As a rule, they do not reduce the size of the tumor, but relieve pain well and remove bleeding.
The safest method of non-surgical treatment is considered focused ultrasound ablation.
It is carried out under the control of a tomograph and consists in heating and destroying the tumor with an ultrasonic beam.
This procedure is non-traumatic and painless, has no side effects, makes it easy to get pregnant and bear a child in the future.
In case of large size and rapid growth of nodes, severe bleeding or necrosis, surgery may be required.
If a woman does not plan to have children, she begins menopause, and the node is growing rapidly, accompanied by constant and heavy bleeding, then it is recommended complete removal of the reproductive organ.
In other cases, an operation is performed to remove uterine fibroids, or myomectomy, There are several types of surgical treatment:
- laparoscopy (through small punctures on the abdomen);
- embolization (through the femoral artery);
- hysteroscopy (through the vagina).
- dieting;
- exclusion of abortion;
- regular examination by a gynecologist;
- timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the genital organs.
Disease prevention:
Do not delay the birth of a child. The optimal age for the first birth is 22-25 years.
By the way, breastfeeding can significantly reduce the risk of neoplasms in the future. But after 35 years, giving birth is not recommended.
From this video you can learn more about uterine fibroids:
It is absolutely impossible to use folk remedies in the treatment without consulting a doctor.
It is better to take care of your health: eat right, do not self-medicate, avoid stress and strengthen the immune system.
Content
Among the gynecological diseases of older women, one of the most common is uterine fibroids. Many confuse it with malignant tumors, but women with such a diagnosis should not panic, because the disease is not oncological. To make sure that it is not so dangerous, it is worth studying the types, symptoms, methods of treatment and prevention.
What is myoma
This pathology is a disease of the female reproductive system, which is manifested by the formation of a benign tumor of the myometrium, i.e. muscular layer of the uterus. There are no cancer cells. The ICD-10 code of the disease is D 25. Doctors know what fibroids are, but the pathogenesis of this pathology has not been fully studied. More often it is noted in women 30-40 years old or just before menopause, i.e. at the age of 50. Often, pathology accompanies an ovarian cyst.
Doctors determine the size of the tumor in centimeters, millimeters, or weeks, as during pregnancy. For example, 12 weeks. This means that the uterus is enlarged, as in pregnancy at 12 weeks. There is a classification of this pathology according to several criteria:
- According to the composition of the tumor - fibroma, or fibromyoma (from connective tissue) and leiomyoma from muscle tissue.
- "On the leg." Separate variety. It can be subserous or submucosal, i.e. grow outside or inside the organ. What distinguishes it is its location “on a leg” - a narrow or wide base that connects it to the uterus.
- Calcined. A tumor covered with a calcium capsule.
The latter classification is determined by location. It turns out to be more complex due to the multiplicity of names:
- interstitial (intra- or intermuscular, intramural);
- submucosal (submucosal);
- subserous (subperitoneal);
- interligamentous (intraligamentary).
Interstitial
Intramural myoma is located in the center of the myometrium, i.e. muscular layer of the uterus. It is characterized by large sizes. In another way, it is called intramuscular or interstitial uterine fibroids. This type of pathology occurs more often than others - 60% of cases. It is characterized by symptoms such as menstrual irregularities, a feeling of heaviness and pain in the genital area (pelvis).
Submucosal
The last place in frequency is occupied by submucosal uterine fibroids - what is it, the gynecologist will tell you. It is diagnosed in 13% of patients with this diagnosis. Its second name is submucosa. This means that the nodules are located practically in the uterine cavity, but under its inner thin shell. It turns out that the tumor bulges out and goes into the lumen of the organ. Because of this, the uterine cavity is significantly deformed.
subserous
The second most common diagnosis is subserous uterine fibroids - observed in 35% of patients. This tumor is subperitoneal, as it is located on the outer part of the organ and develops towards the abdominal cavity. With her, the menstrual cycle is very rarely lost. Subserous fibroids are divided into the following types:
- "Type 0". A knot on a wide base - 0-A, a knot "on a leg" - 0-B.
- "Type 1". Most of the node is located in the serous membrane.
- "Type 2". Most of the tumor is located in the thickness of the myometrium.
Multiple
One of the classifications divides this pathology into single and multiple uterine fibroids. The first case is when the tumor process consists of only one node. The second option is when several neoplasms appear at once. This form is called multi-node. It is diagnosed much more often, while the patient may not even be aware of the disease, because it is asymptomatic. What does a fibroid look like? It represents nodes of different shapes and parameters.
Uterine fibroids - symptoms and signs
Symptoms of different forms of this gynecological disease may vary. Specific signs of uterine fibroids depend on the age of appearance of the neoplasm, its location and size. The growth rate of the myomatous node also affects the manifestation of the disease. More typical symptoms of pathology are as follows:
- pain in the lower abdomen and in the lumbar region between menstruation;
- discomfort and pulling sensations also in the lower abdomen;
- rapid growth of the abdomen and weight gain;
- difficulty emptying the bladder;
- prolonged constipation;
- elevated temperature;
- pain when urinating;
- delay, increased pain in menstruation;
- spotting between periods.

pain
The nature of the pain depends on the location of the tumor. Although sometimes the size of the neoplasm is decisive. With this in mind, pain in uterine fibroids can be as follows:
- With submucous. The pains are either constant aching or cramping. The former are associated with compression of the surrounding fibers by the myomatous node. Cramping occurs before and during menstruation.
- With intramural. This type of myomatous nodes is characterized by prolonged aching pain. They increase during menstrual bleeding. There may also be pain and dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
- With subserous. It often occurs without symptoms, so the pain is minor and rarely appears.
Bleeding
It is easy to distinguish from ordinary menstrual bleeding in uterine fibroids. If during critical days you have to change the gasket more often than 1 time per hour, then this is a cause for concern. The following signs are also considered abnormal:
- periods longer than 7 days;
- severe weakness and fatigue during menstruation;
- the discharge is more abundant and there are many blood clots;
- severe pain in the lower abdomen.
Uterine fibroids - causes
The main reason why uterine fibroids appear is interference in its cavity. These include curettage, a large number of abortions, the installation of spirals. A significant role in the development of the disease is played by hormonal imbalance (high estrogen levels). Today, psychosomatics is considered an important factor in the occurrence of such a disease, i.e. stress, resentment, fears and problems in intimacy with a man. In addition to these main factors, the reasons include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- endocrine diseases;
- bad ecology;
- weakened immunity;
- frequent visits to the solarium, massages;
- use of intrauterine devices for contraception;
- diabetes;
- obesity;
- chronic diseases of internal organs;
- adenomyosis;
- malnutrition;
- irregular sexual relations and lack of orgasm.

How to treat myoma
Scraping is prescribed for diagnosis, echographic methods are used. One of them is ultrasound. Echo-signs can detect changes in the structure of the organ. There are two ways to cure fibroids. The first one is the conservative method. This is where drugs are used. They can only reduce tumor growth. This technique is effective when approaching menopause, when there is a chance that the tumor will begin to regress. If conservative treatment does not bring results, then they switch to surgical methods to remove the nodules or the entire uterus.
Removal of fibroids
If regression of the disease is not observed, then fibroids are removed. They do this in two different ways:
- With the help of organ-preserving surgery. In this case, only the myomatous node is removed by laparoscopy or hysteroscopy. In the second - through the vagina. Find out more about how it's done.
- By removing the entire uterus. This operation is called a hysterectomy. It can be total with the removal of the cervix, or subtotal, when the cervix is left.
Laparoscopy
Surgical methods of treatment include laparoscopic removal of the uterus. This operation is considered more sparing, because it is performed without large incisions on the abdomen. How are uterine fibroids removed? With the help of a cannula, a special tube, gas is injected into the abdominal cavity. As a result, the wall of the abdomen rises above the organs. The surgeon then proceeds to operate with instruments and a video camera. Removal of the uterus takes from 1.5 to 3.5 hours. Laparoscopy is often used to diagnose the disease in order to recognize the nodes. Recovery after surgery is carried out in the clinic.

Treatment without surgery
There are also methods on how to cure uterine fibroids without surgery. They are used in the early stages of the development of the disease. The gynecologist may prescribe the following procedures:
- Embolization of the uterine arteries. With this operation, they stop the blood flow. This is done using a catheter, which is inserted through the femoral artery into the uterus. The procedure is performed without anesthesia. As a result, the tumor node is replaced by connective tissue.
- FUS-ablation. Tumor tissues are heated by exposure to focused ultrasound. The result is the destruction of the tumor - thermal necrosis. The same result is obtained as a result of laser treatment.
Folk remedies
There are several effective folk remedies for uterine fibroids. Only they need to be used in combination with the main methods of treatment. At home, the following traditional medicine has proven itself:
- decoctions from potato flowers;
- douching with soda solution;
- tincture based on a golden mustache;
- decoctions of medicinal herbs - cornflower, motherwort;
- serpentine, chamomile, valerian and St. John's wort.
What is dangerous uterine fibroids
The main thing that is dangerous for uterine fibroids is complications. Bleeding that accompanies diseases causes anemia and even a threat to life. In 1.5-3% of cases, the tumor develops into a malignant one. There is still a small danger. The consequences may be as follows:
- the development of an "acute abdomen" with twisting of the thin "leg" of the tumor;
- tumor necrosis, which requires immediate intervention;
- violation of reproductive function in the form of frequent miscarriages or ectopic pregnancy;
- purulent inflammation in the node and septic complications in more severe cases;
- infertility;
- excretory system disorder.

Prevention
It is better not to treat any disease, but to prevent its occurrence. To do this, you should follow a few simple rules. The main measures for the prevention of uterine fibroids are as follows:
- eliminate stress;
- do not lift weights;
- take vitamins;
- have sex regularly
- do not overheat in the bath, do not sunbathe a lot on the beach or in the solarium;
- eat healthy foods;
- do gymnastics, do yoga or sports;
- quit bad habits;
- regularly visit gynecology;
- plan pregnancy to avoid abortion.
Also find out what is .
One of the most pressing problems for modern women has become such a disease as fibroids.
In this article, you can find out what it is, how to treat it, and whether it is dangerous. In an accessible language, everything about uterine fibroids in women will be described in detail: symptoms and treatment, classification, causes, complications and consequences.
Attention: at the end of the article, live photos of the formations will be provided, so viewing them is not recommended for impressionable and easily suggestible people! Videos of actual operations will also be provided.
First, let's look at the definition of the disease and its varieties.
What is myoma
Uterine fibroids is a disease of the female reproductive system, which is characterized by the formation and growth of a benign tumor in the uterus, namely in its muscular layer. Most often, this disease is found in a woman 30-40 years old or more. But there are more and more cases when this diagnosis is made at a younger age, including in virgins 20-25 years old.
Myoma nodes can be located inside the body of the uterus, this localization variant is found in 95% of cases, and in the cervix in 5% of patients. If the tumor develops from the connective tissue, it is called a fibroma, and if it develops from the muscle, it is called a leiomyoma.
The growth rate of the neoplasm depends on the hormonal background, so hormone therapy is one of the methods of treatment, but surgery is a more effective option to eliminate the problem.
Kinds
Depending on the location relative to the myometrium, the classification of fibroids will be as follows:
- intermuscular (interstitial, intramural) - the node is located inside the muscle layer;
- subperitoneal (subserous) - the node is located near the peritoneum under the mucous membrane of the outer layer of the uterus;
- submucosal (submucosal) - the node is located in the uterine cavity under its inner mucous layer;
- interligamentous (intraligamentary) - the tumor is located between the wide uterine ligaments.

There are different types of nodes, they can be on a leg or on a flat base. By the number of nodes, fibroids can be single or multiple, but most often the appearance of one node entails the appearance of other neoplasms.
By size
Gynecologists indicate the size of fibroids in centimeters, referring to the size of the node itself, or in weeks. If the diagnosis says “myoma 13 weeks”, then the uterus with a myomatous node has increased to the size that is typical for pregnancy at 13 weeks. Based on such criteria, the tumor can be classified into 3 types:
- small sizes– up to 2 cm (4 weeks);
- average- 2-6 cm (10-11 weeks);
- large sizes- more than 6 cm (12 or more weeks).

What is dangerous uterine fibroids
Any tumor is dangerous for the human body, since it is an abnormal neoplasm for it.
In the initial stages, some women still do not fully understand why a benign formation is dangerous, but as it grows, they begin to feel the squeezing of the organs in the small pelvis. In the presence of fibroids, blood circulation in neighboring organs is disturbed, since the formation itself acquires its own vascular network. In addition, fibroids can be a sign of endocrine diseases, which in turn can cause additional health problems.
What happens if you don't treat
Many women who have been diagnosed with fibroids are interested in what will happen if it is not treated. Let's list all the consequences of an indifferent attitude to this disease:
- habitual miscarriages, hypoxia, fetal hypotrophy;
- infertility;
- uterine bleeding, which provoke the development of anemia;
- a neoplasm can develop into a sarcoma, from which a woman can eventually die;
- rapid increase in tumor size;
- torsion of the legs of the myomatous node with malnutrition in it;
- reduced uterine tone, which leads to postpartum hemorrhage;
- hyperplastic processes of various types;
- hydronephrosis or pyelonephritis.
What triggers education
The exact reason why fibroids appear, modern medicine has not yet established, But there are a number of factors that can increase the likelihood of its development:
- genetic predisposition;
- hormonal imbalance;
- hyperplastic processes in the endometrium;
- pregnancy, childbirth and interruption;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system;
- chronic stress;
- diabetes mellitus and diseases of the endocrine system, overweight problems;
- chronic diseases of internal organs and systems, hypertension;
- low physical activity;
- irregular sex life and lack of orgasms.

Let us consider in more detail some of the reasons due to which the appearance of fibroids is most likely:
- excess estrogen, lack of progesterone. Since myoma is a hormone-dependent neoplasm, it can develop against the background of hormonal imbalance. It is only natural that it is most often diagnosed in women of childbearing age, usually with an imbalance of estrogen and progesterone. Obesity only exacerbates the situation, since adipose tissue is also capable of producing estrogen;
- pregnancy, childbirth and abortion. Abortion, diagnostic curettage, difficult childbirth and spontaneous abortions increase the likelihood of a neoplasm, and successful childbirth, especially with subsequent breastfeeding, on the contrary, reduces the risks;
- woman nutrition. Unbalanced nutrition and junk food can disrupt the hormonal balance in the female body. Refined foods, trans fats, and fiber deficiency contribute to an increase in the concentration of female sex hormones. Unhealthy food can lead to obesity and, as a result, to the development of fibroids. A woman needs to eat a lot of vegetables, fruits, seafood, cereals, less fat and sugar;
- inferiority of intimate life. Due to irregular sexual intercourse and lack of orgasms, venous blood stagnates in the pelvic organs, which can lead to hormonal disorders and tumor development.

Oral contraception, mechanical trauma to the reproductive organs, and prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation on a woman's body can also provoke the development of fibroids.
Diagnostics
The doctor may suspect the presence of fibroids during a routine gynecological examination, since the size of the uterus in this disease will be increased. Diagnosis of pathology may include the following activities:
- transvaginal ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Ultrasound can assess the size and shape of the tumor;
- hysteroscopy. During the procedure, the doctor can simultaneously biopsy the affected area and send the resulting material to the histological laboratory;
- laparoscopy. Assign in case of controversial situations, when it is impossible to distinguish uterine fibroids from ovarian tumors;
- CT and MRI. Studies, although informative, are expensive, so they are rarely used.
How does a tumor manifest itself?
In the early stages, the disease may not manifest itself at all, the first may appear when the size of the node reaches 2-6 cm:
- sharp pains in the lower abdomen, which are not associated with the arrival of menstruation. The nature of the pain is cramping, pulling;
- painful periods, although previously they did not have such a feature;
- increased menstrual flow;
- heavy intermenstrual bleeding;
- failure of the regularity of the menstrual cycle, both its lengthening and shortening;
- problems with conception.

The symptomatology of this disease depends on its remoteness, the age of the patient, the size and location of the neoplasm, the rate of its growth, and the presence of concomitant chronic diseases.
Very often, fibroids do not make themselves felt, it can only be detected at the next gynecological examination. By probing the abdomen, the doctor will detect an enlarged uterus and will send the woman for an ultrasound scan, where the echo signs of fibroids will confirm the preliminary diagnosis.
This disease has a number of characteristic symptoms, having discovered which, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor:
- pain in the intermenstrual period, which are felt in the lower abdomen and give to the lower back and limbs;
- menstrual disorders. The duration of the cycle changes, menstrual pain intensifies, the intensity of discharge increases during the regulation, bleeding begins in the middle of the cycle;
- a woman cannot get pregnant for a long time.
If the myomatous node rapidly increases in size or already has an impressive volume, the girth of the abdomen also increases, while the body weight remains practically unchanged. In the lower abdomen, discomfort and aching pains are felt, which increase during psycho-emotional and physical exertion.
Large myoma nodes can put pressure on neighboring organs, thereby provoking constipation, frequent trips to the toilet "in a small way" and painful urination.
If the leg of the myomatous node is twisted, the body of the fibroid may become necrotic, and symptoms of an "acute abdomen" may additionally appear, such as a sharp pain in the lower peritoneum, an accelerated heartbeat, cold sweat, fainting. In such cases, urgent removal of fibroids is performed.

Pathology can affect other organs and systems, which provokes the appearance of such symptoms:
- with frequent bleeding, anemia develops;
- may often get sick and dizzy;
- pain behind the sternum;
- neuroses and neurotic states arise.
If any of the above symptoms appear, you should definitely seek medical help.
Is it curable or not?
Patients who have not previously encountered gynecological problems, having learned about the diagnosis of "myoma", do not have an accurate idea of whether the pathology can be cured or not.
Although uterine fibroids is a tumor-like disease that has a number of characteristics of a tumor, it still has a number of distinctive features that make it possible to treat the disease not only by surgical methods, but also by conservative ones.
The most pleasant feature of this neoplasm is its ability to decrease in size and completely disappear.
The choice of treatment method is carried out individually, depending on the severity of the disease and the characteristics of the body, only in extreme cases, surgical intervention is performed.
How to treat uterine fibroids
There are 2 ways to treat fibroids:
- conservative treatment in which medications and non-invasive procedures are prescribed;
- surgery, in which the operation is performed.
What to do in each case, only the doctor can determine.
How the treatment of uterine fibroids will be carried out will depend on the severity of the pathology, clinical symptoms, the size of the neoplasm, the age of the patient and the intention to have offspring in the future.

Treatment of fibroids with drugs will be effective only under certain conditions:
- with a small size of the node, when the size of the uterus does not exceed 12 weeks of pregnancy;
- if the disease is accompanied by a small number of symptoms;
- when the node has a wide base and is located subserous or inertial.
Myoma can be treated in the early stages, the longer the tumor is present in the body of a woman, the less the opportunity to use conservatism in treatment. In the presence of serious contraindications to surgery, drug treatment is the only way out.
Treatment without surgery includes the following set of measures:
- dieting;
- the use of immunomodulators;
- phytotherapy;
- physiotherapy procedures;
- hormonal drugs.
During drug treatment, a patient with fibroids goes through the following stages:
- inflammations and infections are eliminated;
- the work of the immune system is activated with the help of special preparations;
- diet and daily routine are adjusted;
- the work of the endocrine system is normalized;
- an even psychological background is formed;
- bleeding is eliminated and the anemia caused by it is treated;
- the menstrual cycle is normalized.
Having found a fibroid in a patient, the doctor determines the rate of development of the pathology in a year. If it grows in a year to the size of a 4-week pregnancy, then it is considered fast-growing and is transferred to surgical treatment.
Now consider each of the methods of treatment in more detail.
Medications
Conservative treatment is carried out using the following groups of drugs:
- androgen derivatives;
- gestagens;
- combined oral contraceptives;
- analogues of gonadotropin-releasing hormone aGnRH.

One of the innovative medicines is Esmya, the main active ingredient of which is ulipristal acetate. This medicine for 3 months of treatment in patients who were prescribed surgery, significantly reduces the size of the neoplasm and reduces the intensity of symptoms, and in 50% of cases there was no need for surgery. The tablets have no side effects, and six months after their use, the tumor does not resume its growth.

Now let's take a closer look at drugs from other groups.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists
These drugs introduce a woman into an artificial menopause, suppressing ovarian function with hormones. Agonists of natural gonadotropin-releasing hormones suppress the secretion of sex hormones by the pituitary gland, which affect the activity of the ovaries. The drugs in this group include:
- Buserelin;
- Triptorelin;
- Leuprorelin;
- Goserelin.
Under the influence of drugs, the ovaries stop their activity, ovulation does not occur, the inner uterine layer does not change, and menstruation stops coming. This is a reversible process, after the drug is discontinued, the ovaries resume their work. The course of treatment is six months. During this time, the size of the neoplasm should decrease by 50%, and the symptoms should decrease significantly.
These drugs have a number of negative sides:
- fibroids can fully recover in size after stopping the medication;
- the drug should not be taken for more than six months, as the risk of developing osteoporosis and other complications due to estrogen deficiency increases.
Most often, agonist drugs are prescribed before surgery to reduce the tumor in size.
Antigonadotropins
Most often, Danazol and Nemestran with the active substance gestrinone are prescribed from this series. These medicines reduce the intensity of symptoms, but do not reduce the size of the fibroids. When taking them, a number of side effects are possible:
- increased hair growth on the face and body;
- the timbre of the voice changes;
- rashes appear.

These drugs are prescribed most often in the absence of the effect of hormone therapy.
Gestagens
The drugs in this series include Duphaston, Norkolut and Utrozhestan. They normalize the growth of the endometrial layer in the presence of hyperplasia that occurs against the background of fibroids. Fibroids are treated poorly exclusively with gestagens, they are prescribed only when the neoplasm develops simultaneously with endometrial hyperplasia. The course of treatment is 8 months.
Another drug that contains a progestogen (levonorgestrel) is the Mirena intrauterine device. It is put on for 5 years and in addition to blocking the growth of the tumor, it also has a contraceptive effect.
Antiprogestogens

Operations
Unfortunately, drug treatment can not always give a good result.
If the fibroid cannot be treated with conservative methods, surgery is indicated. To begin with, consider the cases in which an operation is prescribed for myoma.
Indications for surgery
The operation is prescribed under the following conditions:
- the size of the node exceeds the uterus of the 12th week of pregnancy;
- the tumor presses on the nearest vessels and organs, interfering with their normal work;
- neoplasm provokes heavy bleeding;
- there is a very strong pain;
- the leg of the knot twisted, and its death began;
- a submucosal myomatous node appeared;
- in addition to fibroids, endometriosis was diagnosed;
- there is a suspicion of malignant processes in the neoplasm;
- if the tumor grows very quickly, an operation is urgently needed.
Now let's take a closer look at the types of surgical interventions and the situations in which their use is necessary.
Embolization

Recently, a lot of practicing surgeons use the method of uterine artery embolization. This is a minimally invasive intervention, during which an embolus is introduced into the vessel of the uterus, it blocks the arterial lumen. The blood supply to the myomatous node stops, and its tissues die.
This is the most effective method for patients with fibroids who are planning to have children in the future.
Hysterectomy
The most radical method in which the organ is completely removed. There are 3 access options:
- abdominal- the most commonly used method, which involves supravaginal amputation of the uterus or its extirpation. Urinary incontinence is a frequent negative consequence of extirpation. Supravaginal amputation is possible if the cervix is healthy and the nodes between the cervix and uterus are not large;
- laparoscopic;
- vaginal- It is used for small sizes of the myomatous node.

Before the operation or during it, the surgeon determines the advisability of removing the uterus and ovaries along with the uterus. The decision is made individually in each case, taking into account the age of the patient and the presence or absence of neoplasms on the ovaries.
This method is prescribed in such cases:
- fibroids are larger than 13 weeks of pregnancy;
- medical treatment is ineffective;
- the tumor is growing rapidly;
- the ovaries are affected by a tumor;
- acute bleeding began.
Myomectomy
Women who are of reproductive age and still want to have children are initially given recommendations on how to cure myoma with medical methods, if they do not help, then a conservative myomectomy can be prescribed. During this intervention, the myomatous node is exfoliated to healthy tissue. The intervention is performed laparoscopically or abdominally.

Fuzz ablation
This is a non-invasive method of treating pathology, which is carried out under the control of MRI. During the procedure, the cells of the myomatous node are heated by an ultrasonic pulse until they are completely destroyed.

The process is carried out in several stages. Initially, the doctor examines the neoplasm and plans the operation using an MRI. At the second stage, under the control of the MRI machine, the doctor begins to heat the cells of the node to a certain temperature with ultrasound pulses. After cell death, the specialist cools the tissues. Depending on the size of the tumor, there may be several such sessions. The procedure itself takes about 4 hours. A follow-up MRI is done with contrast.
Since FUS ablation is a non-invasive technique, it has many positive aspects:
- no need for anesthesia and postoperative care;
- there are no complications and adverse reactions, such as bleeding, fever and intoxication;
- both the uterus and the reproductive function of the woman are preserved;
- fast recovery;
- no relapses;
- the method is also effective in the treatment of large nodes;
- myoma decreases in size immediately after the session;
- you can quickly get rid of uncomfortable symptoms.
During the procedure, the patient lies motionless on her stomach. In the event of any discomfort, she immediately informs the attending physician. The procedure should not cause burning, stabbing or shooting pain, therefore, the appearance of such symptoms should be immediately reported to the medical staff conducting the treatment.
Folk remedies to help
Folk methods of treatment come down only to the use of tampons and douching with herbal infusions and decoctions at home.
None of these methods will help get rid of the underlying internal causes that provoked the development of fibroids. The use of any alternative treatments for this disease should be discussed with your doctor without fail.
Prevention
If you belong to the beautiful half of humanity, then no preventive measures can 100% protect you from the occurrence of fibroids. The only thing that can be in your power to reduce the factors that provoke the growth of fibroids. There are several basic recommendations for women who do not want to face this disease:
- make annual visits to the gynecologist regular, it is better to visit a specialist 2 times a year;
- annually do an ultrasound of the organs of the reproductive system;
- have sex regularly and achieve an orgasm at the same time;
- prevent abortions, and the use of hormonal contraceptives will help protect against unwanted pregnancy;
- control weight, lead an active lifestyle and play sports;
- take vitamin-mineral complexes with antioxidant action, which include vitamins A, E, C, iron, zinc, iodine, selenium.
A few words about pregnancy

Women of reproductive age who have been diagnosed with fibroids always have a number of questions regarding the compatibility of this disease with the ability to have children. We will provide answers to the most popular of them.
Is it possible to get pregnant?
You can get pregnant if you have fibroids in your uterus.
Everything will depend on the size of the tumor and its location. If it does not prevent the fertilized egg from passing through the fallopian tube and gaining a foothold in the uterine wall, then conception will occur. It is important that the entire process of bearing a child is under strict medical supervision.
In the first 2 trimesters, due to hormonal changes in the body of a woman, a slight growth of the myomatous node may occur, but in the last months of pregnancy, the fibroids do not grow, but only lend themselves to destructive changes.
What are the risks to fetal health
Fibroids can disrupt blood circulation and nutrition of the walls of the uterus, which affects the ability of the myometrium to contract properly, so the presence of a neoplasm in the uterus increases the risk of miscarriage.
Premature termination of pregnancy spontaneously or according to indications is the main threat to the fetus, but due to tumor growth, intrauterine growth retardation, fetal hypoxia, premature or prolonged labor can occur, which is also a serious risk for future offspring.
Photo
Finally, we will give you some photos of myomas so that you understand how it looks in real form.
Impressive people do not look!